What is gel electrophoresis?
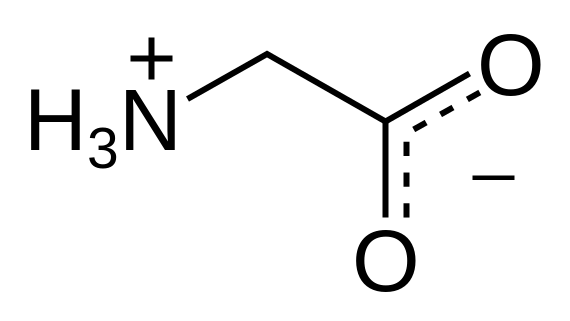
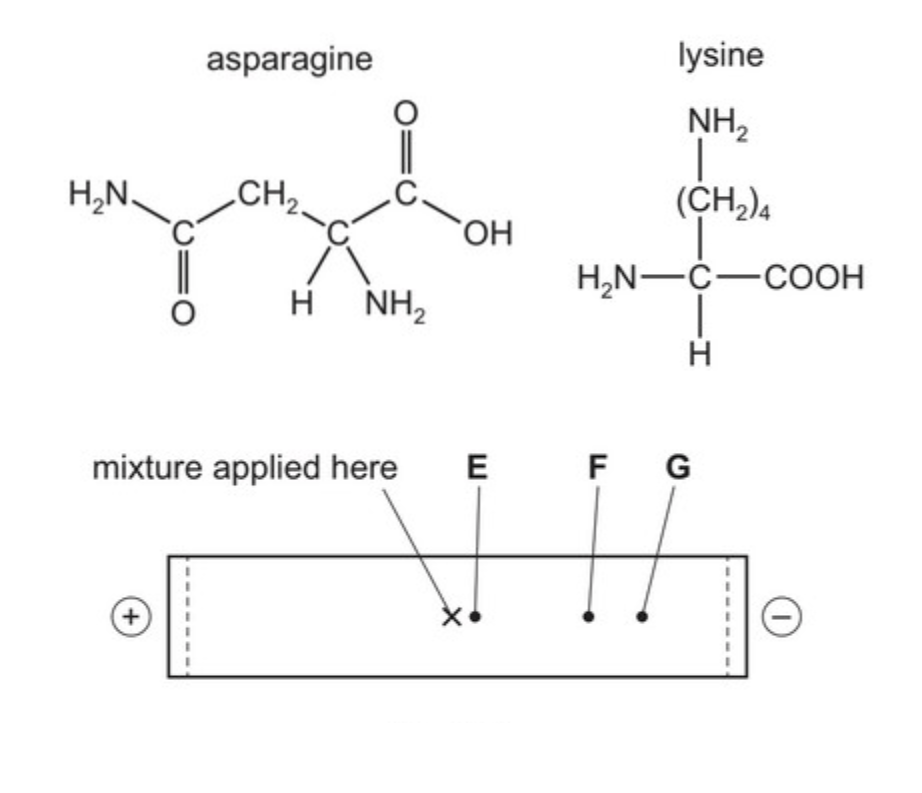
Gel electrophoresis is an analytical technique that separates ions in an electric field and is used extensively in biochemical analysis to separate, identify, and purify proteins, amino acids, and peptides.
In simple terms, different amino acids are put in the middle of a gel at a certain pH. A voltage is applied across the ends of the gel. Amino acids that are positively charged at the particular pH will move towards the negative terminal and those negatively charged will move towards the positive terminal.