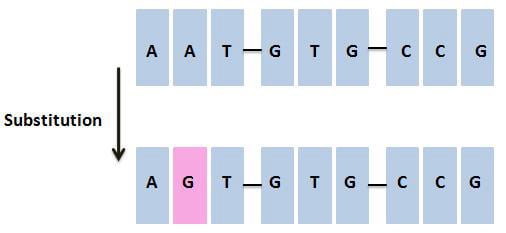
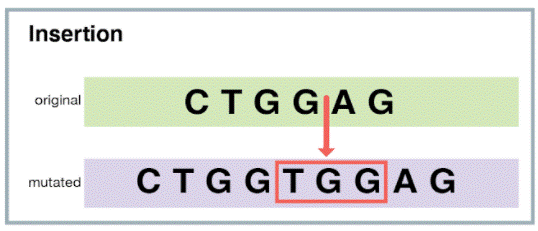
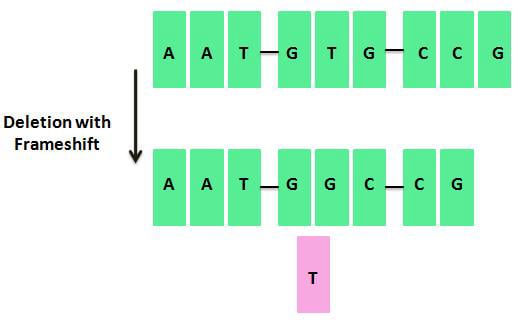
Substitution mutations
- This occurs when one base in the DNA sequence is replaced by another.
- For example, if the original sequence is CAA TTT GAA CCC, a substitution could change it to CAA TAT GAA CCC. This is known as a mis-sense mutation.
- However, a substitution may not always change the amino acid sequence because the genetic code is degenerate, meaning that multiple triplets can code for the same amino acid. For example, TTT and TTC code for lysine.
- If the mutation results in a STOP codon, a shortened polypeptide will be formed. This is known as a nonsense mutation.