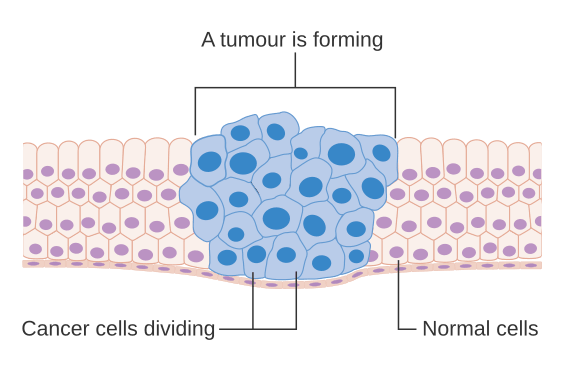
Steps in tumour/cancer formation
- Mutation: Cancers start with changes (mutations) in genes that control cell division. Tumour-suppressor genes are switched off and proto-oncogenes mutate to become oncogenes.
- Cellular Response: Cancerous cells do not respond to signals from other cells and continue to divide.
- Immune System Evasion: Cancerous cells are not removed by the immune system.
- Rapid Mitosis: Cancer cells undergo rapid mitosis.
- Tumour Growth: The tumour enlarges, and cells change their characteristics.
- Blood Supply: The tumour gets a blood and lymph vessel supply.
- Metastasis: Tumour cells spread in the blood and lymph to other body parts, invading other tissues and forming secondary cancers.