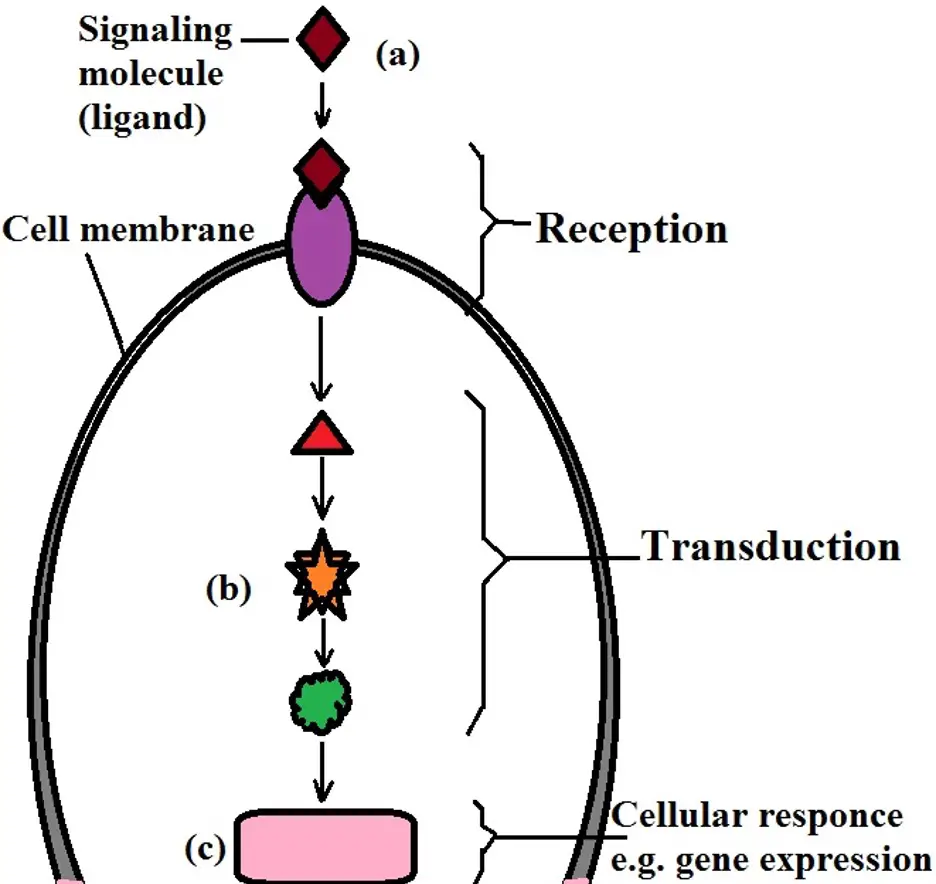
Overall steps in cell signalling
- A stimulus causes cells to secrete a specific chemical called a ligand. The hormone glucagon is an example of a ligand.
- The ligand is transported to the target cells. Signaling molecules are usually small for easy transport, and in the case of hormones, the transport system is the blood system.
- The ligand binds to cell surface receptors on the target cells. The receptors are protein molecules located on the cell surface membrane.
- The binding of the ligand causes the shape of the receptors to change, transmitting the signal to the second messenger in a process called transduction.
- An enzyme cascade reaction is stimulated, resulting in the response.