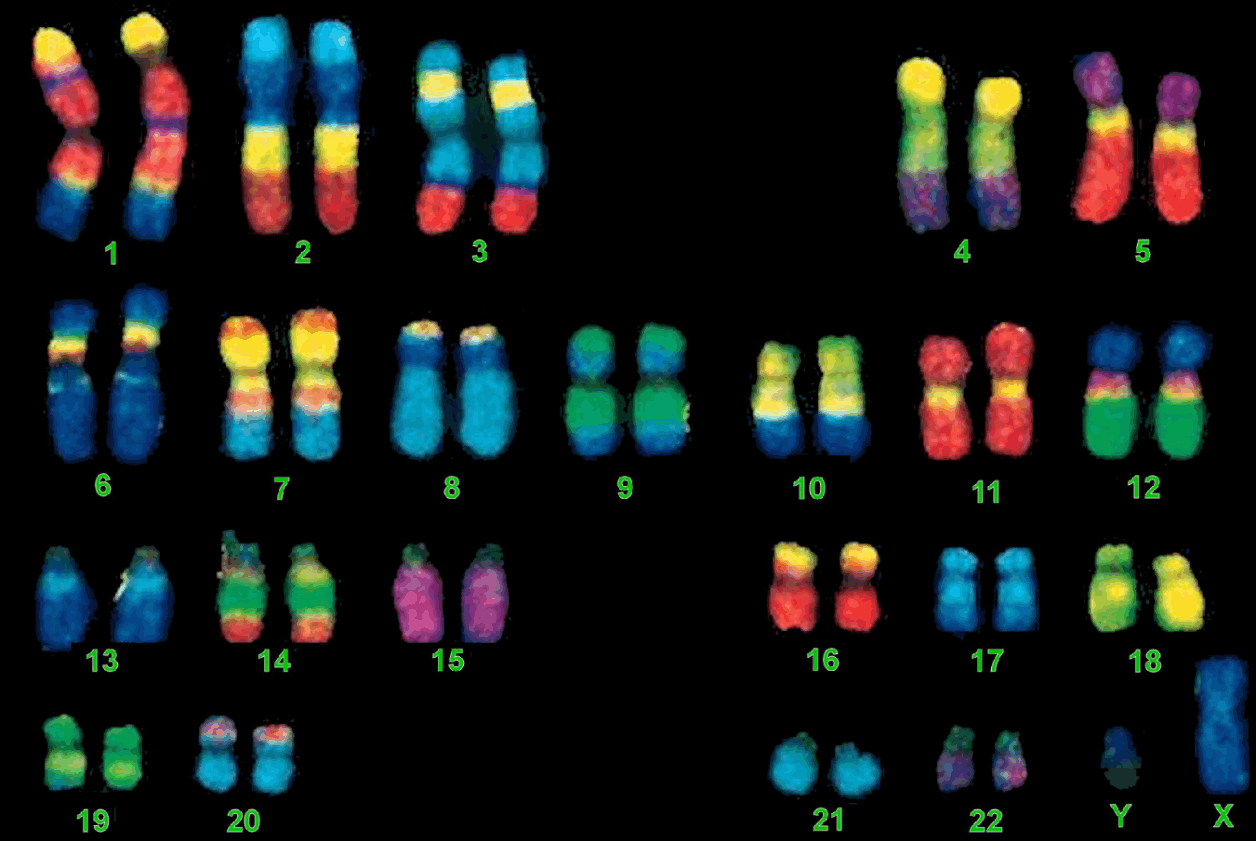
Homologous chromosomes
- Homologous chromosomes are pairs of chromosomes within diploid cells that share the same structure and gene arrangement (same genes at the same loci).
- Homologous chromosomes may possess different versions (alleles) of the same genes.
- In other words, homologous chromosomes represent a "set" of chromosomes in a diploid cell.
- Homologous chromosomes pair up during prophase I in meiosis to form bivalents.