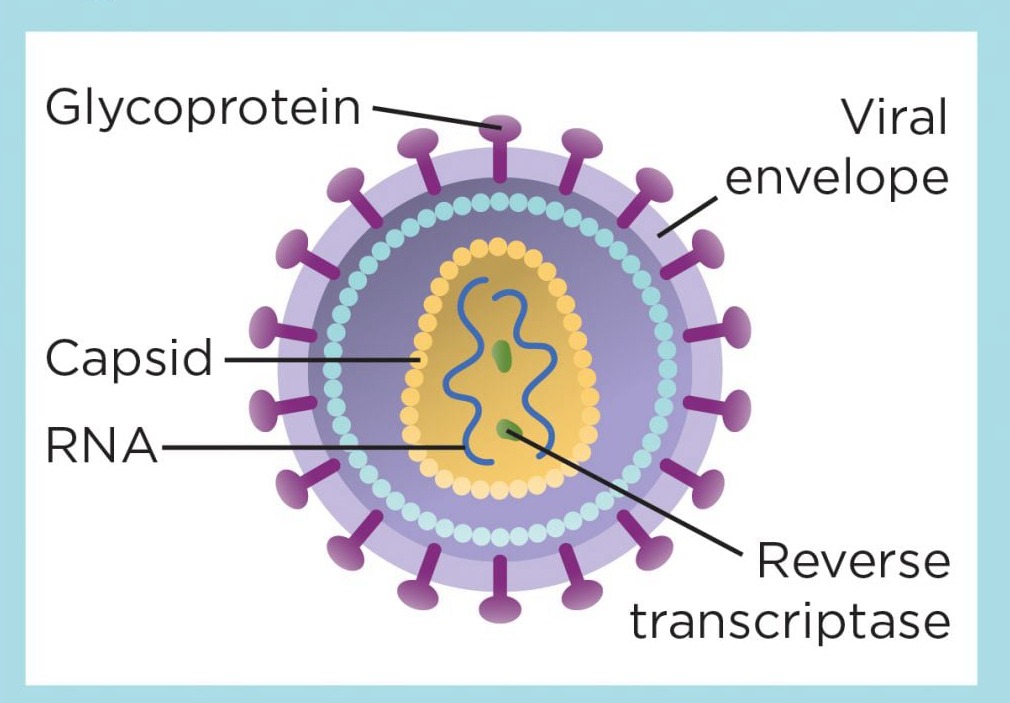
How the HIV virus works
- HIV is a retrovirus, so its genetic material is RNA, not DNA. Once inside a host cell, the viral RNA is converted into DNA and added into the host cell's DNA.
- The virus infects and destroys cells of the body's immune system, specifically T-helper lymphocytes, causing their numbers to gradually decrease.
- When the numbers of these cells are low, the body is unable to defend itself against infection, allowing a range of pathogens to cause a variety of opportunistic infections.
- The onset of opportunistic infections is known as AIDS.