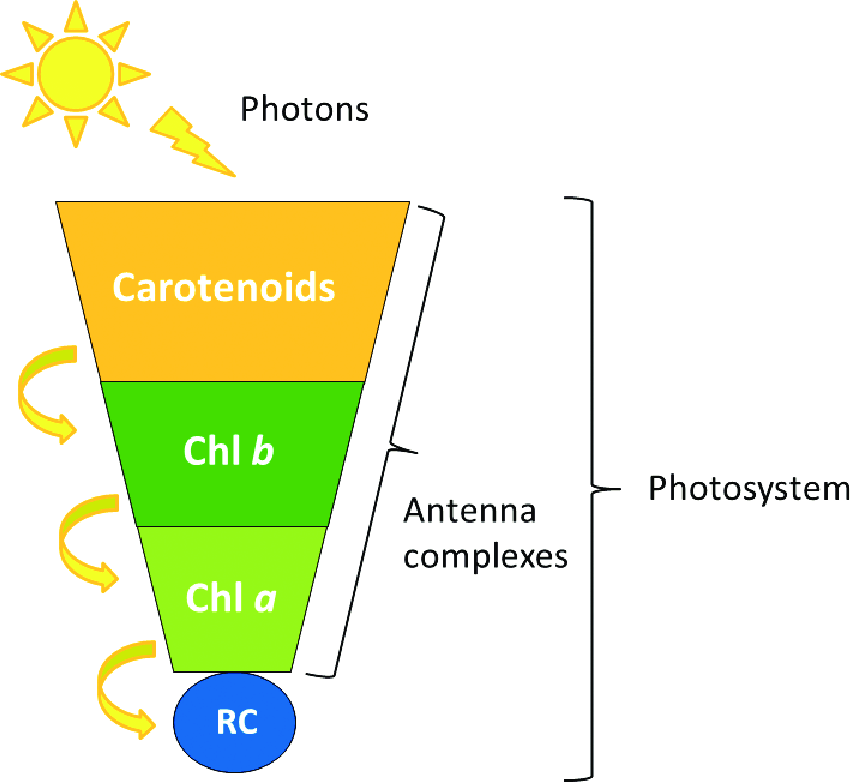
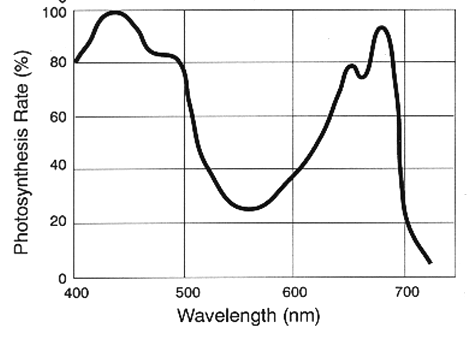
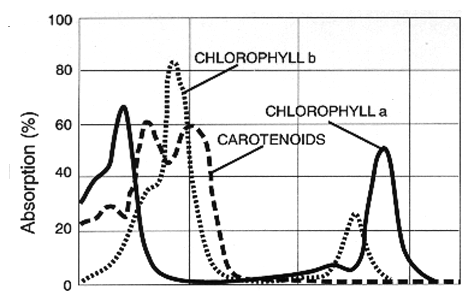
What are chloroplast pigments?
- Chloroplast pigments are colored substances that absorb energy from certain wavelengths (colors) of light.
- The most abundant pigments are chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b.
- Chlorophyll a absorbs mostly violet-blue and orange-red light whereas chlorophyll b absorbs mostly blue and yellow light.
- Other pigments are carotene, which absorbs blue light and xanthophyll, which absorbs blue-green light.
- The pigments are placed together in an antenna complex to maximise absorption of light. The light energy they absorb are converted into excitation energy which is passed to the reaction centre.