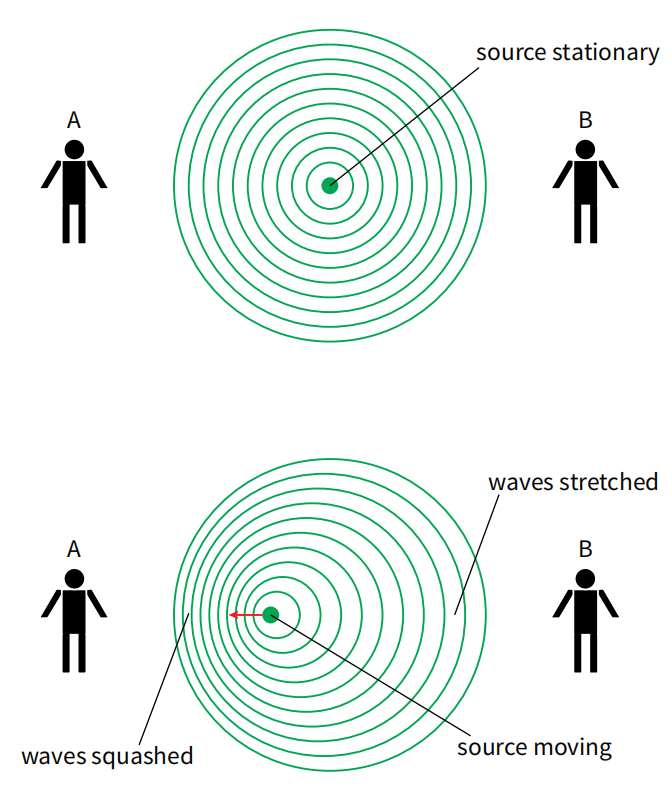
Why does the Doppler effect occur?
- When a wave source is stationary, the waves it emits spread out uniformly in all directions. An observer at any point will receive these waves at the same frequency as they were emitted.
- When a wave source moves towards an observer, the waves in front of the source are compressed. This compression leads to a shorter observed wavelength and a higher observed frequency.
- When a wave source moves away from an observer, the waves behind the source are stretched out. This stretching results in a longer observed wavelength and a lower observed frequency.
- The observed frequency (\(f_{o}\)) can be calculated using the equation \( f_o = f_s \times \frac{v}{(v \pm v_s)} \), where \(f_{s}\) is the source frequency (original frequency) and v is the speed at which the source is moving away/towards the observer.
- The minus sign is used when the source is moving towards the observer and the plus sign is used when the source is moving away.