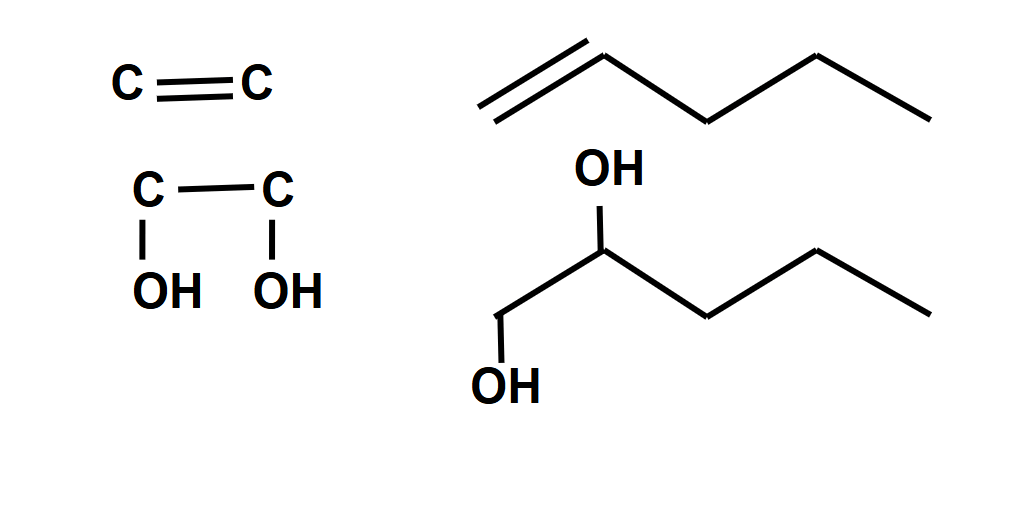
Oxidation under hot concentrated KMnO4/H+
- The C=C double bond in the alkene breaks down entirely. The products that form depend on what is bonded to the carbon atoms in the C=C double bond.
- If a carbon atom is bonded to two hydrogen atoms, it oxidises to form a CO2 molecule.
\( \text{H}_2\text{C}=\text{CH}_2 + 6[\text{O}] \rightarrow \text{CO}_2 + \text{CO}_2 + 2\text{H}_2\text{O} \) - If a carbon atom is bonded to one hydrogen atom and one alkyl group, it oxidises to form a CO (aldehyde) group first, which oxidises again to form a COOH (carboxylic acid) group.
\( \text{RHC} = \text{CHR} + 2[O]\rightarrow \text{RCHO} + \text{RCHO} + 2[O]\rightarrow \text{RCOOH} + \text{RCOOH} \) - If a carbon atom is bonded to two alkyl groups, it oxidises to form a C=O (ketone) group.
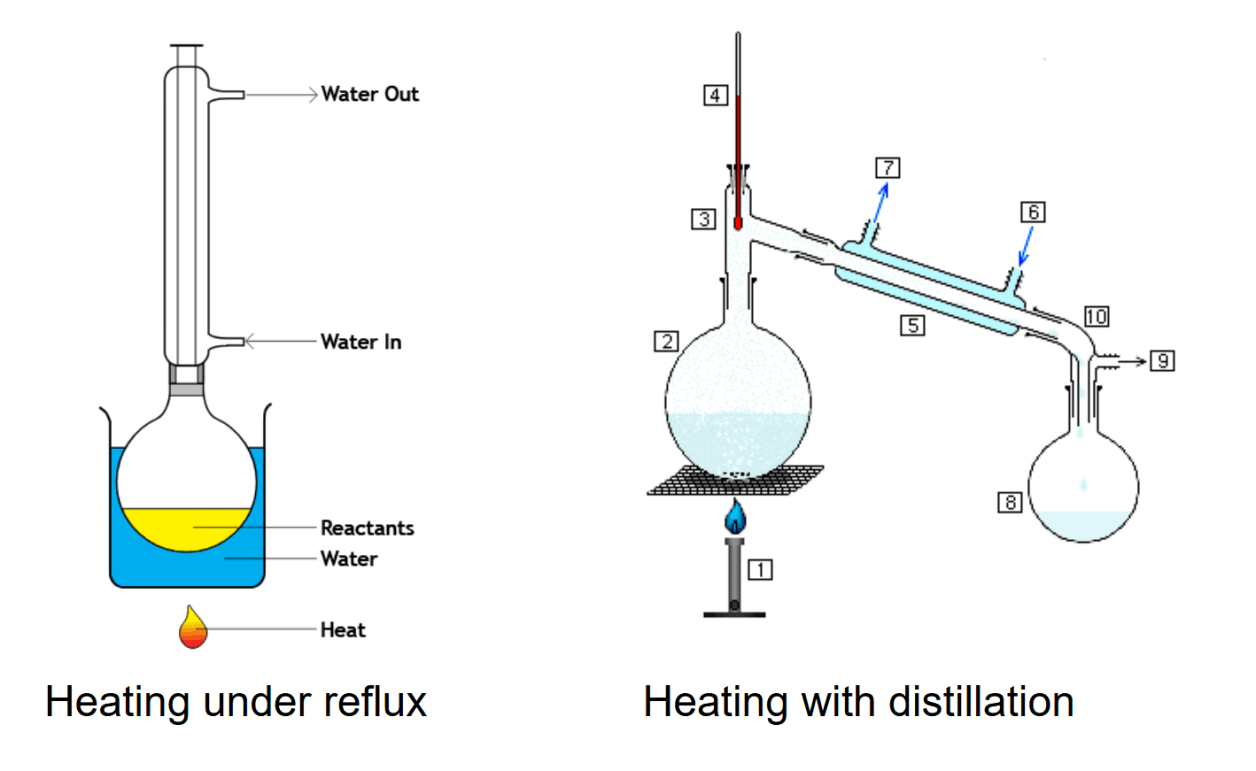
\( R_1 R_2 C = C R_3 R_4 + 2[O]\rightarrow R_1 (CO) R_2 + R_3 (CO) R_4 \) - To obtain aldehydes, the solution must be heated with a distillation apparatus. This is done to collect the aldehyde vapour before it oxidises again to form carboxylic acids.
- To obtain other oxidised substances, the solution must be heated under reflux.