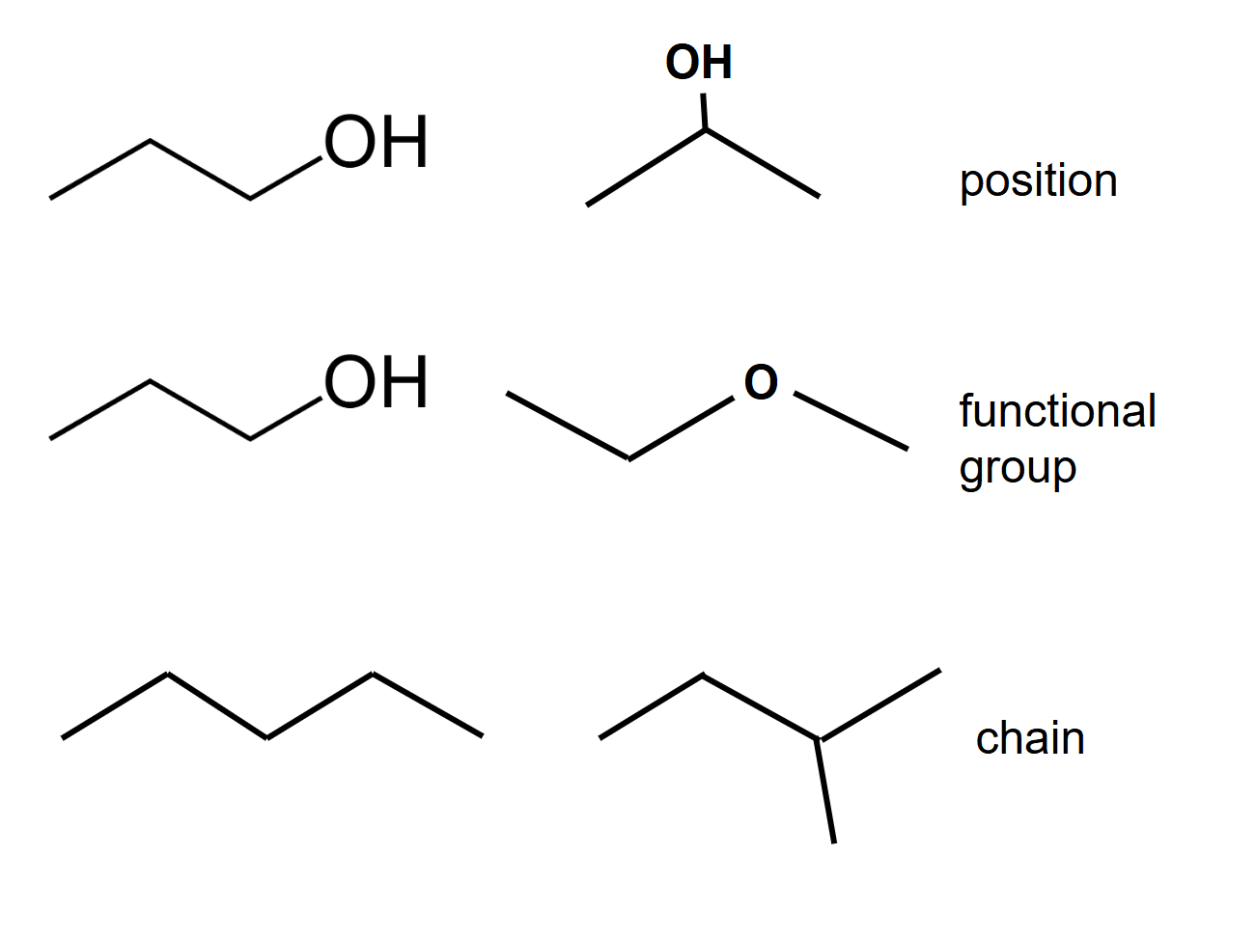
Structural isomerism
- In structural isomers, the chemical formula remains the same but the structural formula changes.
- Position isomerism occurs when the location of the functional group varies in each isomer.
- Functional group isomerism occurs when there are different functional groups present.
- Chain isomerism occurs when isomers differ in the structure of their carbon 'skeleton'.